-
UNITED STATES
North America
South America
Europe
- Belgium (FR)
- Belgium (NL)
- Denmark
- Deutschland
- Europe
- España
- France
- Ireland
- Italia
- Nederland
- Norge
- Polska
- Россия
- Suomi
- Sverige
- United Kingdom
- Schweiz (FR)
- Schweiz (CH)
- Türkiye
Middle East / Africa
Asia / Pacific
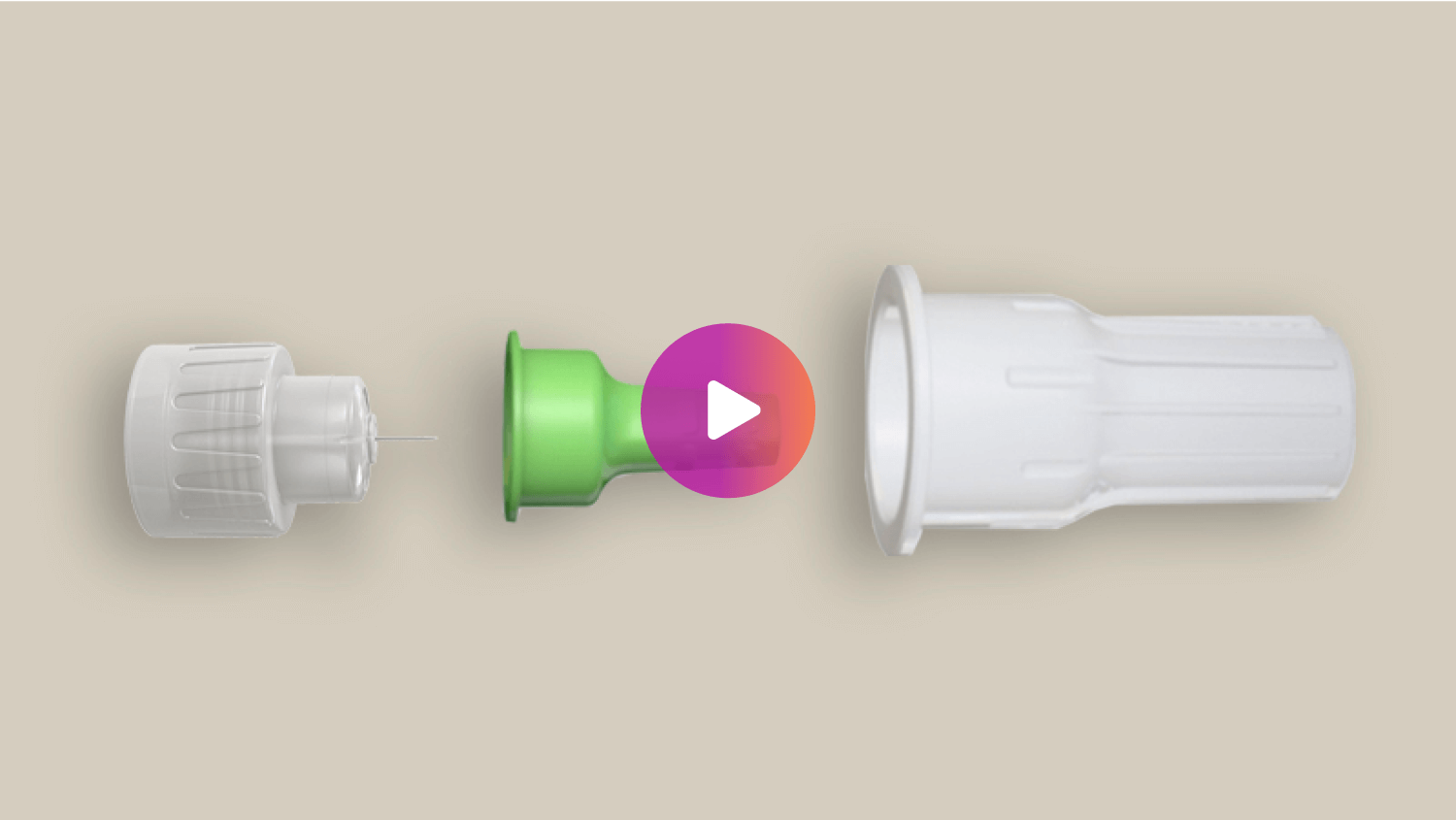
NanoTM 2nd Gen Pen Needles can help your patients deliver insulin correctly1
Insulin injection mistakes are more common than you may think2*
A study showed that people with diabetes were making at least 1 mistake in how they inject insulin.2*
of patients apply
too much injection force2*
The most common mistake was applying too much force against the skin when injecting, which can lead to intramuscular (IM) injection.1-2*† Intramuscular injections may affect proper insulin absorption, increase the risk of hypoglycemia, and lead to increased pain.3
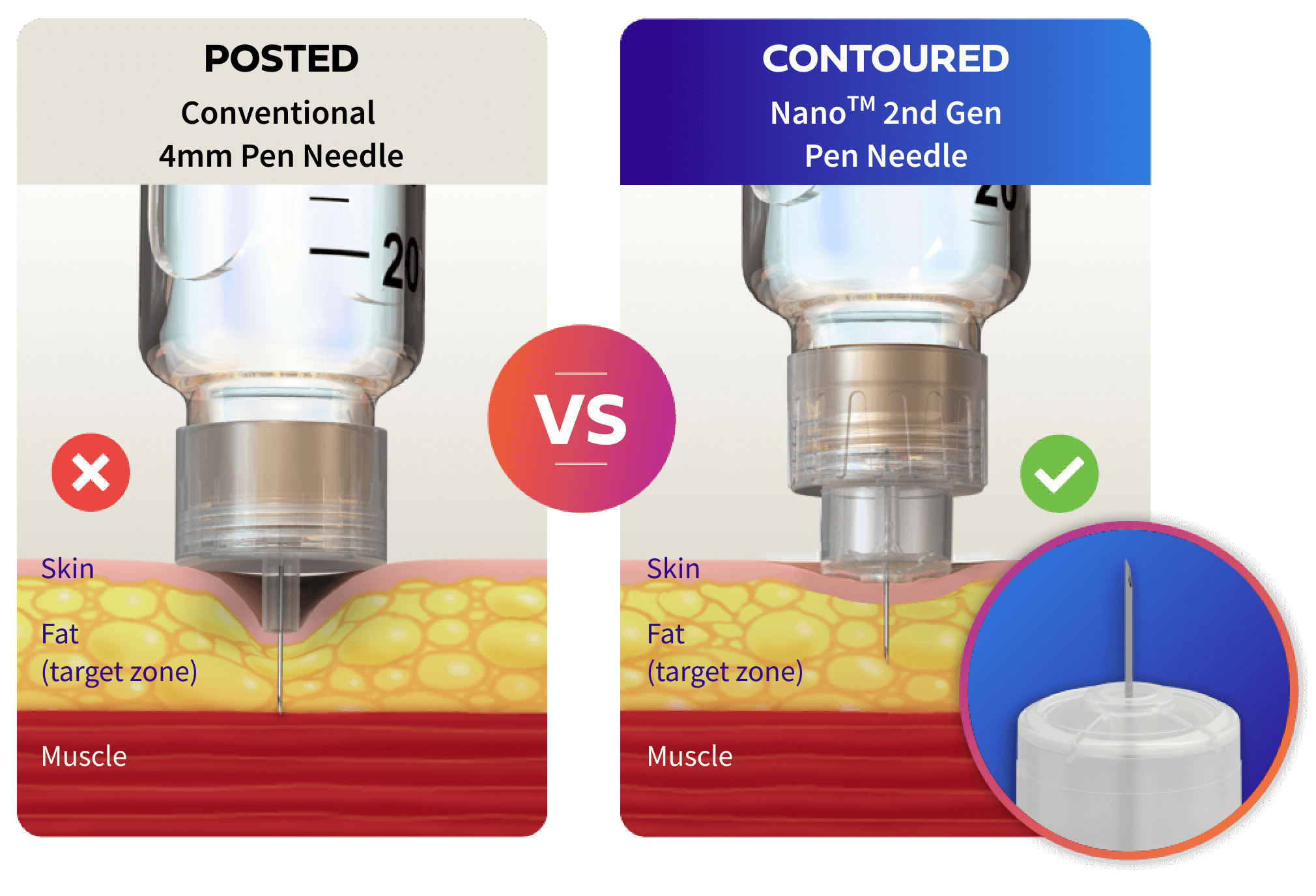
Help your patients deliver their insulin correctly with a contoured needle base
The NanoTM 2nd Gen Pen Needle with its unique contoured base is estimated to reduce intramuscular injection risk by

vs other 4mm posted
base pen needles.1‡
Explore the innovative features
of the NanoTM 2nd Gen Pen Needles
Patients reported greater comfort and ease of use compared
to other pen needles studied overall.4§
Consistency with the contoured base
The unique contoured base pen needle is designed to help compensate for the common challenge of applying too much injection force and deliver a more consistent 4mm target injection depth.1‡

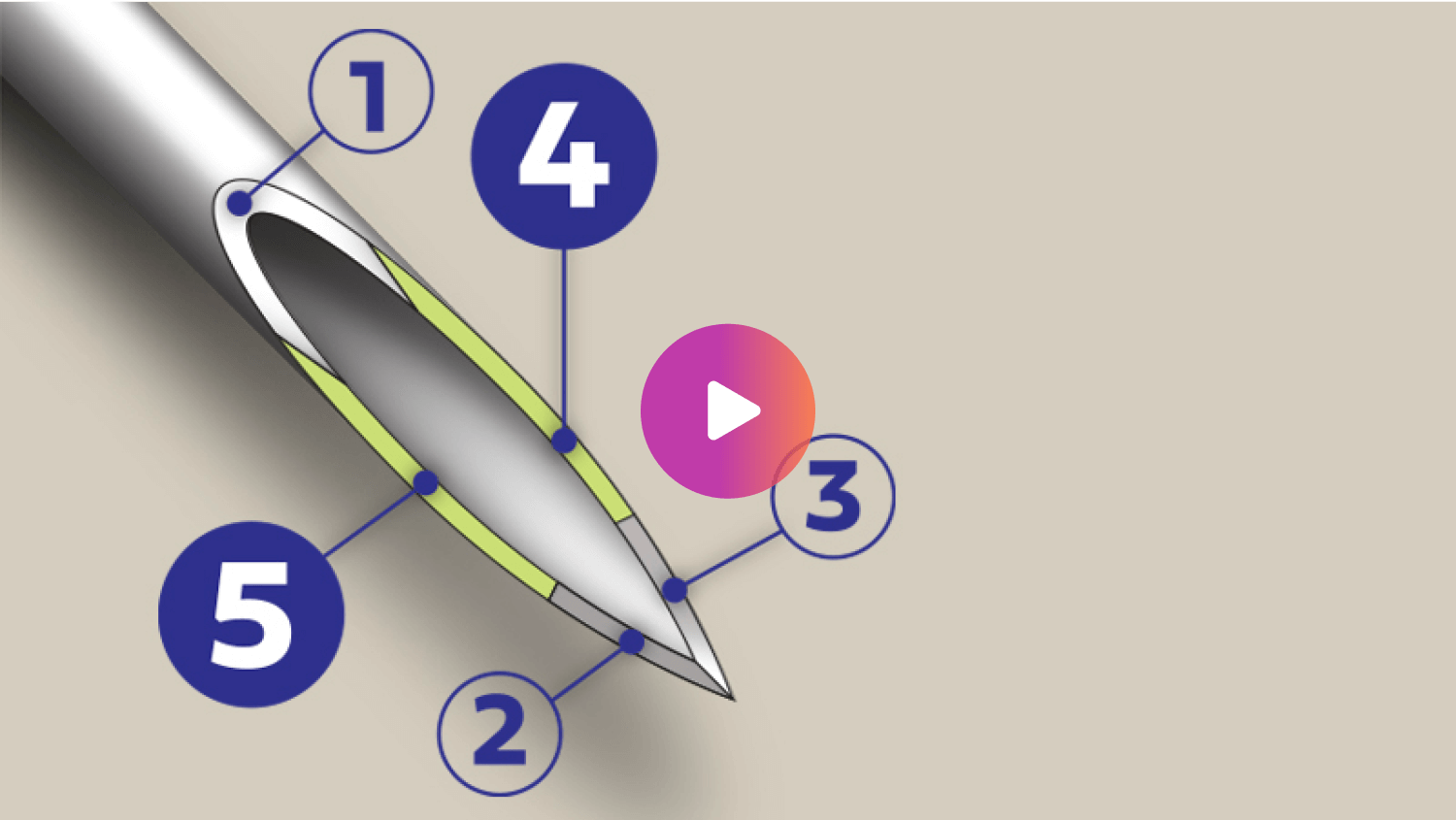
Comfort with a 5-bevel tip
The 4mm needle with a 5-bevel tip can offer a more comfortable and less painful injection experience, compared to similar length 3-bevel pen needles.5¶
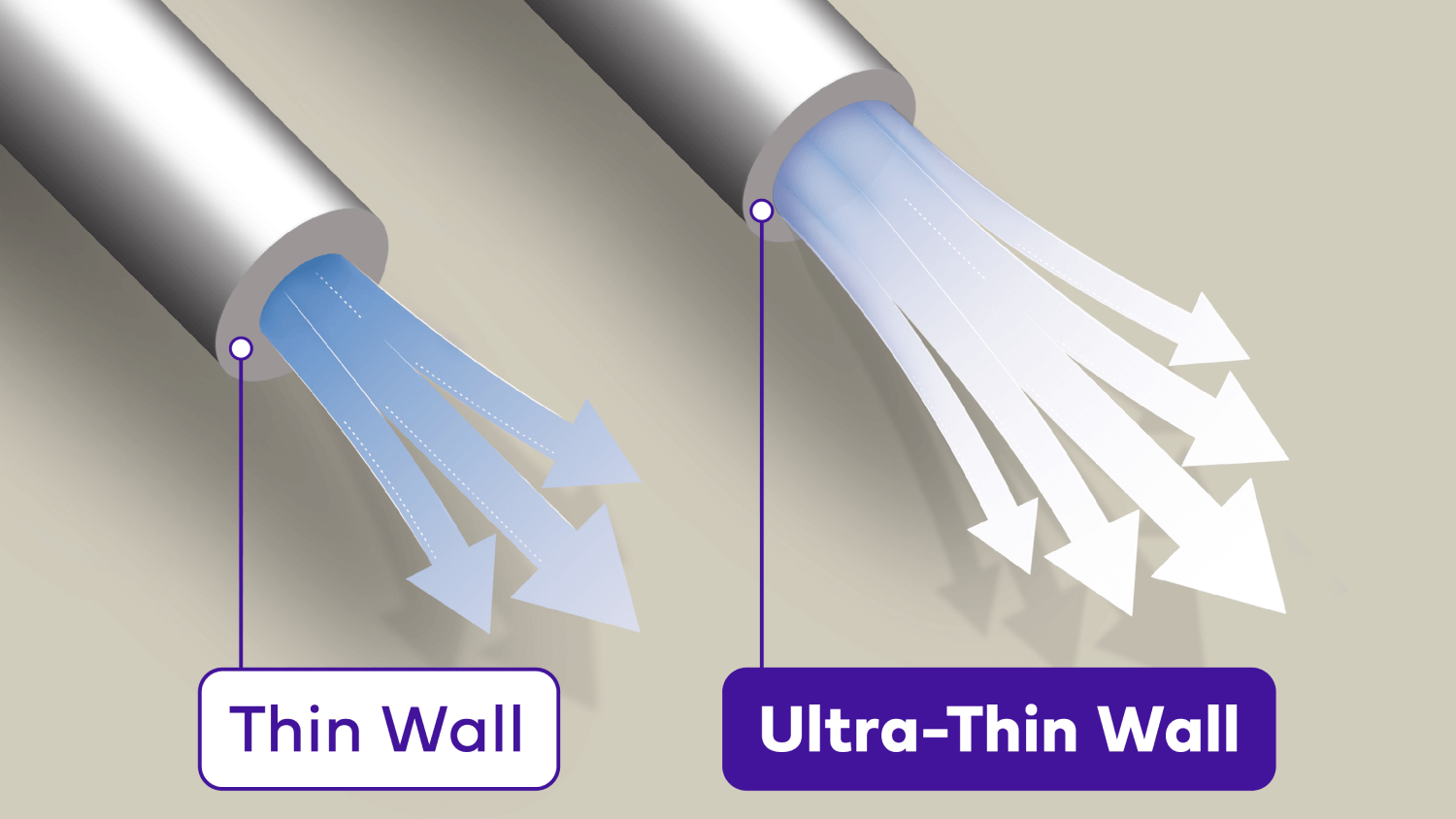
Confidence with Ultra-Thin wall
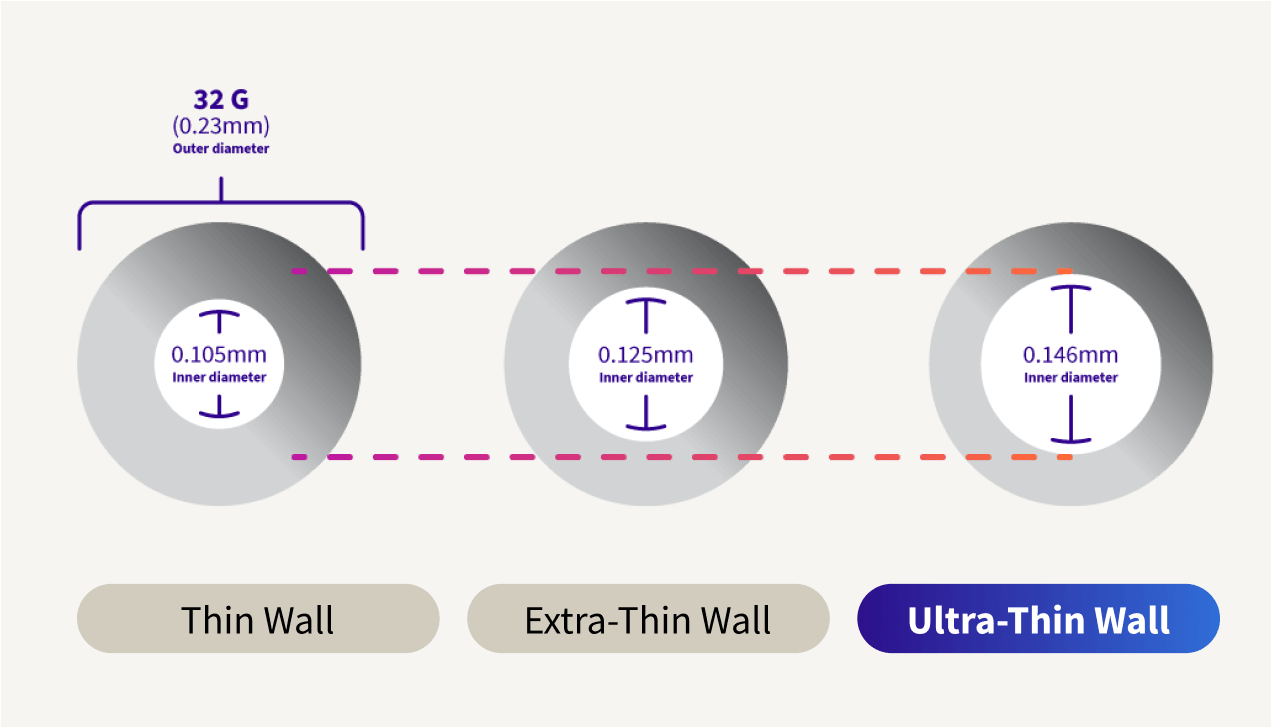
Ultra-Thin wall technology increases the flow of insulin, giving patients greater confidence the complete dose was delivered.6#
Ultra-Thin wall is the highest ISO standard for a 32G pen needle inner diameter.7
Designed for ease of use
The wider outer cover is easier to attach to a pen device and the larger inner needle shield is easier to grip to remove before an injection.4§#
NanoTM 2nd Gen Pen Needles are compatible with widely used pen injection devices8
See Our Compatibility Chart
Our products are covered
More than 9 out of 10 health plans have coverage for embecta pen needles and insulin syringes.9 Search for NanoTM 2nd Gen in your system when prescribing or dispensing.
Help your patients experience the difference of a contoured needle base.
Order Samples*230 patients with diabetes surveyed as part of a cross-sectional observational behavioral study in Canada.
†The study used in-silico probability model of needle penetration depth for posted-hub 4mm pen needles and average human tissue thickness measurements across a range of injection forces and recommended sites, pooled across gender and BMI.
‡To precisely locate injection depth, 1188 injections were administered in swine across a range of clinically relevant injection forces using 20µl of iodinated contrast delivered with Nano™ 2nd Gen vs three 4mm posted-hub pen needles. Intramuscular injection risk was calculated through an in silico probability model, using needle penetration depth and published average human tissue thickness measurements.
§226 patients with diabetes on insulin treatment were studied with a 150 mm visual analog scale (mean scores of >0 mm; clinically significant difference of ≥5 mm). NanoTM 2nd Gen demonstrated superiority vs. all comparator groups combined for feeling more comfortable throughout injection experience and for overall ease of use. [Comfort (P <0.05) (Mean +18.0 mm, 95% CI, +11.6 to +24.3 mm)]; [Easier (P <0.05)(Mean 19.9 mm, 95% CI, +13.8 to +25.9 mm)].
¶86 patients with diabetes used to evaluate differences between 5-bevel and 3-bevel pen needle tips across pen needles (PN) of equal length and gauge. The 5-bevel PN would be considered more comfortable if the 95% lower bound for the percentage of insertions was greater than the 95% upper bound. After subjects were informed, the 5-bevel PN was selected more often than the 3-bevel PN for greater comfort (p = 0.01) in home use. When patients were blinded to the PN bevel designs, no differences were found for ease of insertion (37.1%, 36.8%), comfort (37.1%, 37.6%).
#226 patients with diabetes on insulin treatment were studied with a 150mm visual analog scale (mean scores of >0mm; clinically significant difference of =5mm). NanoTM 2nd Gen demonstrated superiority vs all comparator groups combined for ease of attachment [(P<0.05) (mean +21.8mm, 95% CI, +16.1 to +27.6mm)].
||198 patients with diabetes were included in this prospective, multicenter, randomized, open-label, 2- period, crossover study to evaluate differences in perceived thumb force and in confidence that the full dose of insulin was delivered, between the participants’ usual pen needle (PN) and the corresponding extra-thin wall (XTW) pen needle. Significant differences favoring XTW pen needles were seen for perceived thumb force and confidence that the full dose was delivered by 28.4mm (95% CI, 23.7-33.2), and 24.4mm (95% CI, 19.7-29.1), respectively; (all, P<0.001).
References
1. Rini C, Roberts BC, Morel D, et al. Evaluating the impact of human factors and pen needle design on insulin pen injection. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2019;13(3):533-545.
2. Bari B, Corbeil MA, Farooqui H, et al. Insulin injection practices in a population of Canadians with diabetes: an observational study. Diabetes Ther. 2020;11(11):2595‑2609.
3. Frid AH, Kreugel G, Grassi G, et al. New insulin delivery recommendations. Mayo Clin Proc. 2016;91(9):1231‑1255.
4. Whooley S, Briskin T, Gibney MA, et al. Evaluating the user performance and experience with a re-engineered 4 mm x 32G pen needle: a randomized trial with similar length/gauge needles. Diabetes Ther. 2019;10(2):697-712.
5. Hirsch L, Gibney M, Berube J, Manocchio J. Impact of a modified needle tip geometry on penetration force as well as acceptability, preference, and perceived pain in subjects with diabetes. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2012;6(2):328-335.
6. Aronson R, Gibney MA, Oza K, et al. Insulin pen needles: effects of extra-thin wall needle technology on preference, confidence, and other patient ratings. Clin Ther. 2013;35(7):923-933.
7. Stainless steel needle tubing for the manufacture of medical devices—requirements and test methods. ISO 9626. 2016.
8.Pen Needle Compatibility Status Summary with Diabetes Care & Non-Diabetes Drug Delivery Devices. Document Number: 149OTH-0004-20 Rev Y – 2025-11-18.
9. Fingertip Formulary, as of 05/16/2023.
Compatible with widely used pen injection devices1* |
|
|---|---|
Lilly |
KwikPen (Basaglar, Humalog, Humulin, Lyumjev, Rezvoglar), Forteo, Tempo Pen |
Novo Nordisk |
FlexPen (Novolin, NovoLog), FlexTouch (Fiasp Levemir, Tresiba), Ozempic, Saxenda, Victoza, Xultophy, NovoPen Echo |
Sanofi |
SoloStar (Admelog, Apidra, Lantus, Merilog, Toujeo), Soliqua |
Biocon Biologics |
Kirsty |
Medtronic |
InPen |
Viatris |
Semglee |
|
*Listed brands are owned by third parties. Reference: 1. Pen Needle Compatibility Status Summary with Diabetes Care & Non-Diabetes Drug Delivery Devices. Document Number: 149OTH-0004-20 Rev Y – 2025-11-18. |
|